Everything you need to know about Electrical wiring!
Residential
electrical wiring systems begin at the service entrance, which consists
of the utility's power lines and equipment that supply power to the property.
The electricity is delivered via an electric meter, which keeps track of how
much energy is consumed in residence and is used to calculate the monthly
electric bill. The utility company's jurisdiction ends with the meter in most
cases. Following that, the G3 Electric offers best wiring solutions at your ease.
Service
Entrance:
The
apparatus that supplies electrical repair to the house is known as the
service entry. The typical residential service consists of three wires: two
120-volt cables (for a total of 240 volts) and one grounded neutral wire. A
service drop is a collection of cables that are hung from the ceiling. A
service lateral is lateral that is routed underground service. A service drop
connects to the house at a service head, also known as a above ground service,
which is located on the roof or outside wall.
Electric
Meter:
The
electric meter, which may be situated on an outside wall or located inside the
home, is where power enters the house via the underground or above grand
service. The meter keeps track of all the electricity used in the house, which
is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). One kWh of power is used by a 100-watt
light bulb that burns for ten hours. Meters can be analogue or digital.
However, most modern meters are digital and can be read by the utility provider
remotely.
Main
Service Panel:
The
main service panel, often known as the breaker box or circuit breaker panel, is
responsible for distributing power to all circuits in the building. Each
circuit contains a breaker that can cut electricity to the circuit if it
experiences a short circuit or overload. Fuse boxes may be used instead of
breakers in older dwellings. Although fuses are just as effective as breakers,
breakers are now used in most new panels.
It's
worth mentioning that power is always flowing from the service lines to the
electric meter and then to the main service panel. Before operating on some
sites, the power provider must switch off the electricity. The main breaker at
the service panel can turn off the electricity going out to the residential
circuits, but it has no effect on the power coming in.
Electrical
Wire Color Coding:
Both
the outside sheathing of bundled electrical cables and the individual
conduction wires within cables or inside conduit are color coded. Understanding
the color-coding method can assist you in determining what the wire is utilized
for and maintaining uniformity within an electrical system.
The
cable's color reflects the size of the wires inside the cable as well as the
cable's amperage rating. For example, 15-amp circuits require white-sheathed NM
wire, but 20-amp circuits require yellow NM cable.
Individual
conducting wires are frequently colored to reflect their standard or preferred
application rather than their size or rating. Black and red wires, for example,
are commonly used for current-carrying or "hot" connections, while
white wires are typically grounded "neutral" conductors. Grounding
wires are made of green-insulated and bare copper wires.
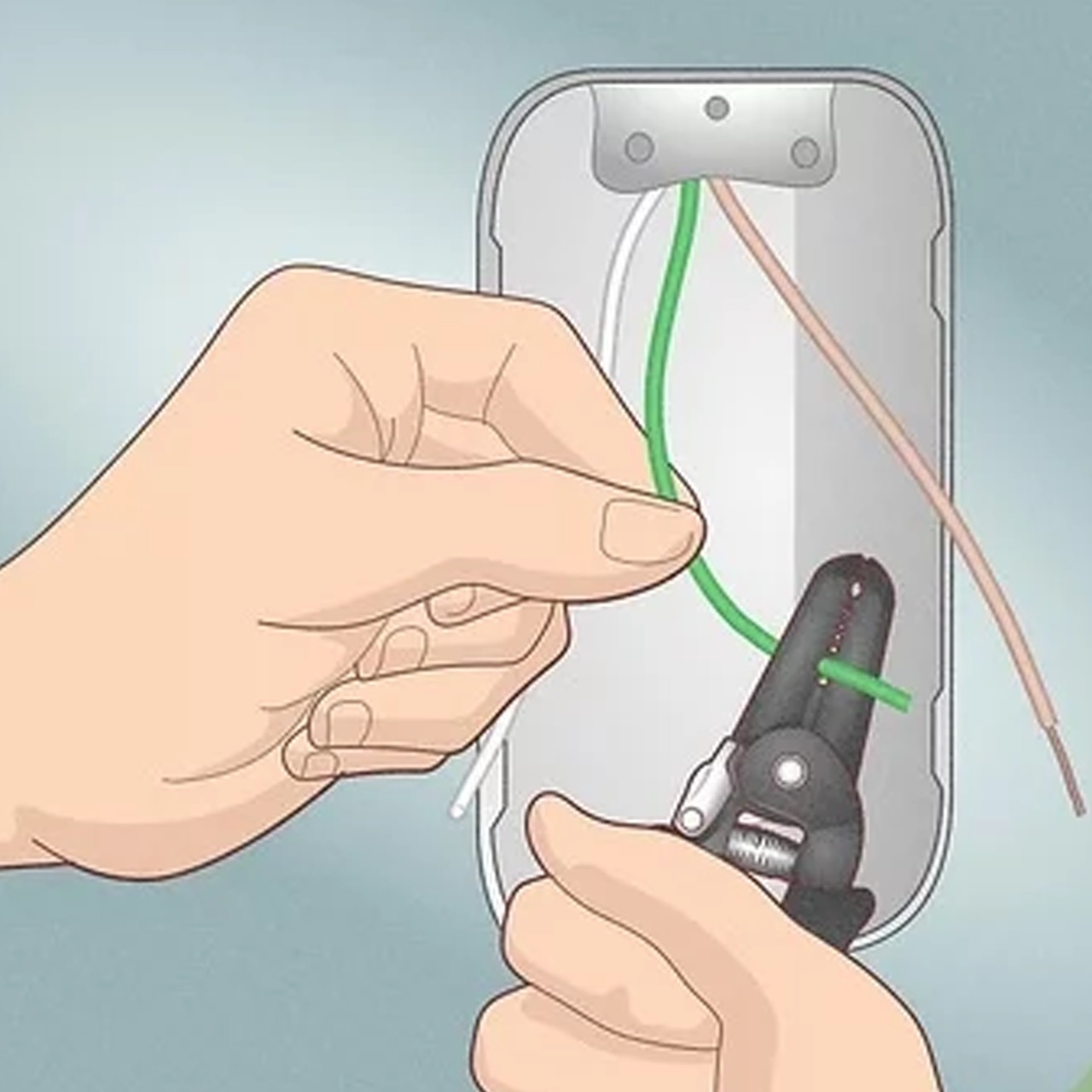
How to Strip Electrical Wire:
The plastic insulation around the wire's metalcore must be removed while stripping the electrical wire. It's critical to do this carefully to avoid damaging the metal. The method is straightforward, but it necessitates the use of a specialized wire stripping instrument and knowledge of how to operate it. For every wiring project, this is an essential skill—and tool—for DIYers to have.
Wiring an Electrical Circuit Breaker Panel:
The
power distribution point of a home's electrical system is the electrical panel,
often known as the service panel. This is where all the house's various
circuits receive power and are protected by breakers or fuses. A licensed
electrician should wire an electrical panel, but DIYers should have a
fundamental understanding of how a panel works and the importance of breakers
in any system.
G3
Electric which located at 10520 YONGE STREET RICHMOND HILL, ON, Canada
and has branches in Ontario and Toronto ensures provide top-notch services to
all its customers. You can also contact at 416-371-0447 to enjoy great deals
and amazing services related to electrical repair.
Address:- 10520 YONGE STREET RICHMOND HILL, ONTARIO CANADA





Comments
Post a Comment